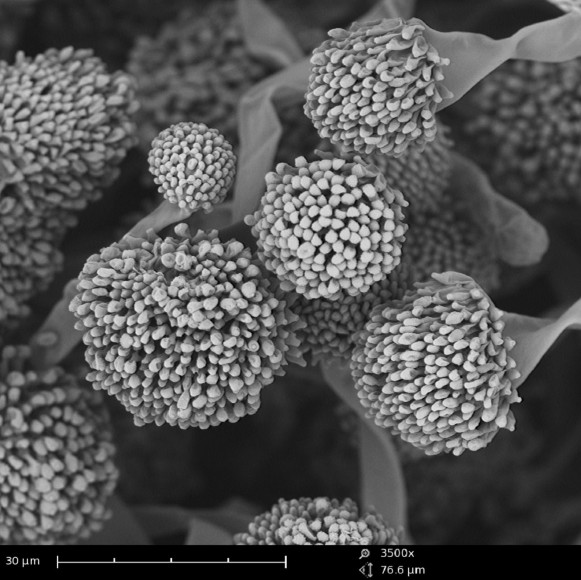
Scanning tunneling microscope stm type of microscope whose principle of operation is based on the quantum mechanical phenomenon known as tunneling in which the wavelike properties of electrons permit them to tunnel beyond the surface of a solid into regions of space that are forbidden to them under the rules of classical physics the probability of finding such tunneling electrons.
Laser scanning microscope facts.
Capturing multiple two dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the.
As the confocal optical system only detects fluorescence that is present at a location extremely close to the sample s focal point the optical resolution in.
The confocal laser scanning microscope clsm is a microscope which focuses only on a single focal plane and the unfocused plane will not be visualized.
Clsm combines high resolution optical imaging with depth selectivity which allows us to do optical sectioning.
However fluorescent probes.
With confocal laser scanning microscopy clsm we can find out even more.
In the past the traditional laser microscope excited the whole thickness of the sample resulting in saturated blurry images and sometimes visualizing false colocalization images.
Optical electron and scanning probe microscopy along with the emerging field of x ray microscopy.
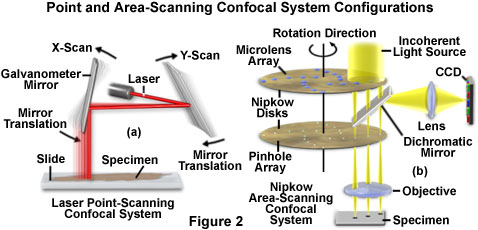
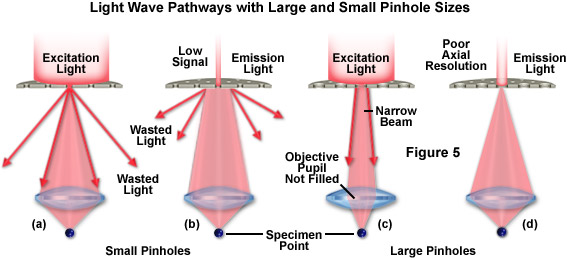
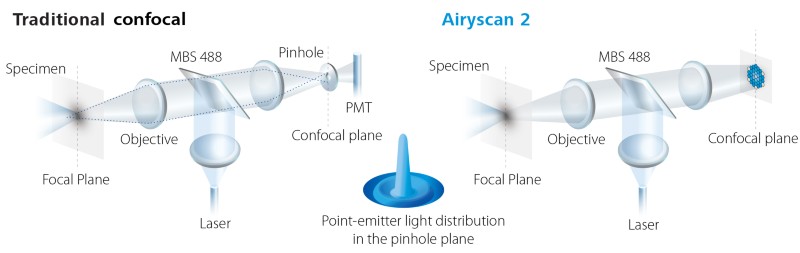
The photons of light released are passed through a pinhole before being.
This means that we can view visual sections of tiny structures that.
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye.
Many laser scanning microscopes utilize the confocal optical system where a pinhole is placed at the focal point in order to condense light emitted from a sample in front of the detector.
Basic microscope optical system characteristics have remained fundamentally unchanged for many decades due to engineering restrictions on objective design the static properties of most specimens and the fact that resolution is governed by the wavelength of light.
There are three well known branches of microscopy.
The electron source and electromagnetic lenses that generate and focus the beam are similar to those described for the.
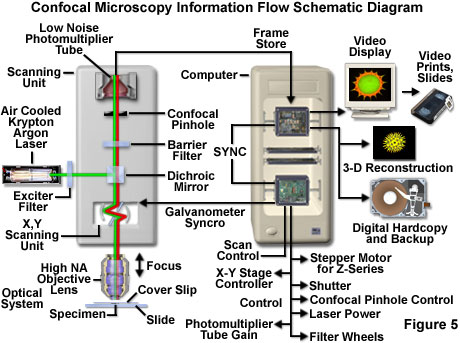
Confocal microscopy most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy clsm is a powerful technique to produce sharp images of a sample that would otherwise appear blurred when viewed under a conventional microscope reconstruction of three dimensional structures from images obtained by this technique is possible by taking a large number of images at different depths a process known as.
The laser scanning microscope passes a laser beam through an objective lens to illuminate a single point in an object.
Fluorescent microscopy not only makes our images look good it also allows us to gain a better understanding of cells structures and tissue.